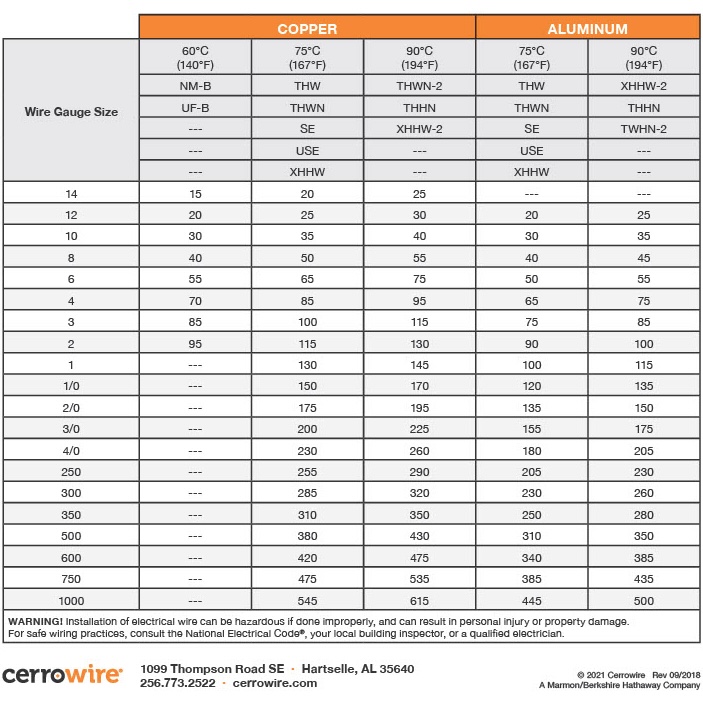
Ampacity is the maximum current that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating. Current is measured in amperes or “amps.” You must use the correct size wire for the circuit’s current (load) requirement to prevent the wire from overheating.
The number and type of electrical devices connected to a circuit determine the ampacity requirement of the conductor. Usually, a general-purpose house circuit is designed for 20 amps. Lighting circuits may be designed for only 15 amps.
To calculate the load requirement for a circuit, first, add up the wattage of all the electrical devices that will be on the circuit. Then, divide the total wattage by the system’s voltage (homes are typically 120 or 240). That will give you the required current or amps.
For example, if I have five 100-watt light bulbs in my kitchen (500 total watts) running on a 120-volt circuit, then my amp load is 4.16 (500 watts / 120 volts). In this case, I am well under my walls’ typical 15 amp-rated wire.